

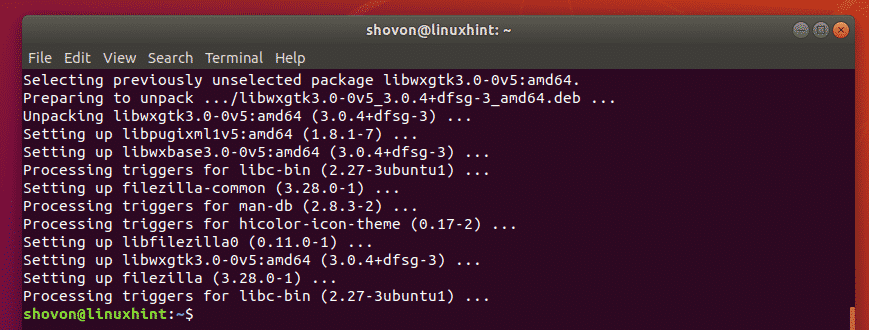
The post How to install Ubuntu software (.deb) package from the command line. Many of the intricacies involve in the process are abstracted from the view of the Linux user. The common way is through the Ubuntu software centre. There are a couple of ways to get (install) software applications (app) installed in Ubuntu. The “ dpkg” utility is a low-level package tool use in Ubuntu (and other debian-based distriutions) for directly installing software packages (in this case, the. deb file via the command-line interface (CLI) or the Terminal, you need to follow the instructions below. Open the terminal (SHORTCUT: _ Ctrl+Alt+T _ ) and enter the command: They are commonly used in examples because they are simple and ubiquitous. Three such programs are apt, apt-get and apt-cache. A significant part of APT is defined in a C++ library of functions APT also includes command-line programs for dealing with packages, which use the library. This deb package contains all the dependencies an application needs to be successfully installed, which can be done through the terminal using the following steps: APT is a collection of tools distributed in a package named apt. Also some app distributors for the Ubuntu platform would rather choose to distribute their apps by [providing downloadable Ubuntu/Debian (.deb) package from their websites. If you want to use the apt command for deb files, use it like this: sudo apt install. The apt command uses the dpkg command underneath it, but apt is more popular and easier to use. Many of the intricacies involve in the process are abstracted from the view of the Linux user.īut some software apps cannot be found (and installed) in the official Ubuntu software repository. If you want to install deb packages in the command line, you can use either the apt command or the dpkg command. There are a couple of ways to get (install) software package(s) or applications (apps) installed in Ubuntu.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
